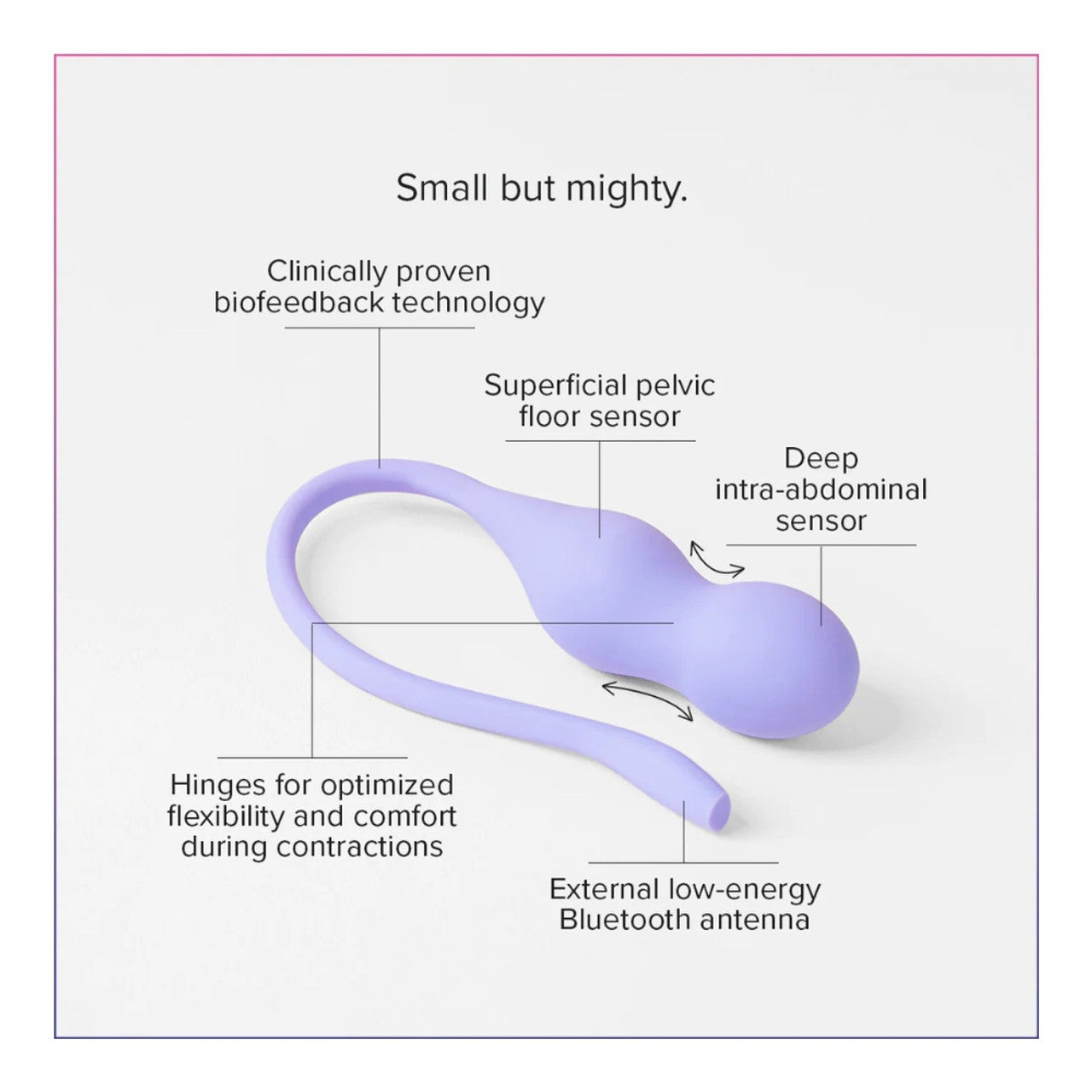
Author: Katie Lyons - Aviiana's Nutrition Coach
When you hear "creatine," what comes to mind? I used to think it was just for bulky bodybuilders—like Arnold Schwarzenegger—chugging protein powders to bulk up. But creatine isn't just a guy thing anymore. Women are taking over the squat racks, picking up dumbbells, and making strength training a priority! And creatine can definitely support those muscle gains and strength improvements.
But here's the really exciting part: while creatine is well-known for enhancing muscle growth and strength performance, recent research reveals it offers a lot more. Did you know it can also boost mood and brain function? 
Whether you're aiming to enhance your athletic performance, manage the ups and downs of perimenopause, or maintain strength and mental sharpness after menopause, creatine can be a beneficial part of your health strategy.
Let’s dive into what creatine really is, how it works, and why it’s worth considering for more than just muscle gains.
So, What Exactly Is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found primarily in your muscles, as well as in the brain, and it's made from three amino acids: arginine, glycine, and methionine. Think of it as your body’s internal energy reservoir. When you’re engaging in high-intensity activities like sprinting, lifting weights, or even when your brain is working overtime, creatine steps in to provide the extra energy needed by quickly regenerating a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which fuels all our cellular activities.
Our bodies naturally produce creatine, and we also get small amounts of it from food sources like red meat and fish. However, while creatine from diet and natural production is enough for basic bodily functions, it’s not typically enough to fully saturate our muscle stores. People who have low levels of creatine — such as vegetarians — appear to benefit most from creatine supplements.
That’s where supplementation can come in. It can help ensure your muscles are fully saturated, giving you better performance and recovery, not just in the gym, but also in day-to-day tasks.
The Unique Benefits of Creatine for Women
Research shows that creatine supplementation can enhance cognitive performance, stabilize mood, and offer neuroprotective benefits, especially under cognitive stress. This means that, beyond its well-known advantages for physical performance and recovery, creatine also plays a significant role in supporting our brain health.
It helps sustain mental energy and sharpness, boosts mood, and can even supports bone health, making it a versatile and valuable supplement for women throughout their lives.
With these benefits in mind, let’s look at how creatine can support women during perimenopause and post menopause.
Perimenopause: Support Energy and Mood
Perimenopause is a time of hormonal upheaval, and it can come with a whole host of symptoms—fatigue, mood swings, brain fog, and muscle loss, just to name a few. Creatine may help:
- Fight Fatigue: Feeling tired all the time is one of the most common complaints during perimenopause. Creatine works by boosting your body’s ATP levels—the molecule responsible for energy production in your cells. This can give you the energy you need to get through your day without feeling constantly drained.
- Lift Your Mood: Research suggests that creatine may have mood-boosting properties, potentially helping to reduce symptoms of depression and improve overall emotional well-being. With the emotional rollercoaster that perimenopause can bring, this is a benefit many women would welcome.
Post-Menopause: Stay Strong and Sharp
After menopause, the body undergoes significant changes, particularly when it comes to muscle mass and bone density. Creatine can help mitigate some of these changes:
- Preserve Muscle Mass: Muscle loss accelerates after menopause due to decreased estrogen levels, but creatine supplementation can help maintain and even build lean muscle mass. This is crucial not just for staying fit but for maintaining functional strength as you age—making everyday tasks easier and promoting overall independence.
- Support Bone Health: Weak bones are a real concern post-menopause, with many women facing an increased risk of osteoporosis. Interestingly, creatine has been shown to support bone density, making it a great addition to your overall strategy for bone health.
- Boost Cognitive Function: Creatine isn’t just good for the body—it’s also good for the brain. Many women experience "brain fog" after menopause, but creatine has been found to improve memory and mental clarity, keeping you sharp as the years go by.
But Do You Need to Exercise to Reap the Benefits?
You might be wondering, “Do I need to be lifting weights or hitting the gym for creatine to work?” While creatine is definitely a go-to for athletes, you don’t need to be a gym regular to see benefits. Creatine can help support muscle mass, bone health, and brain function, even if you aren’t doing intense physical activity. That said, combining it with exercise, such as resistance training, can enhance its benefits even further.
If you are looking for a Wellness Program that helps you Stay Active, improve Sleep, and reboot your Mindset. Join the Aviiana Wellness Program and book a FREE 15min consultation with me.
Getting Started with Creatine: What You Need to Know
If you're considering adding creatine to your routine, here’s a straightforward guide to help you get started.
What Type of Creatine Should I Take?
Creatine Monohydrate is often referred to as the "gold standard" for several reasons:
- Extensive Research: It is the most studied form of creatine, with substantial evidence supporting its effectiveness and safety.
- Proven Efficacy: Research consistently shows that creatine monohydrate effectively boosts muscle strength, power, and exercise performance.
- Cost-Effective: It is generally more affordable than other forms due to its simple manufacturing process and widespread availability.
- High Bioavailability: It’s well-absorbed and utilized by the body, making it effective for increasing muscle creatine stores.
- Safety and Tolerability: With a long history of use and a strong safety profile, it is a trusted option for both athletes and those seeking general health benefits.
Creatine monohydrate typically comes in powder form and mixes easily with water, smoothies, or even coffee.
How Much Should I Take?
For most women, a daily dose of 3-5 grams is effective. While some opt for a "loading phase" of 20 grams per day for 5 days to quickly saturate their muscles, this step is optional. Starting with the standard dose allows your body to gradually build up its creatine stores.
When Should I Take It?
Creatine can be taken at any time of day, but it's often recommended to take it with food to improve absorption. Although some studies suggest that taking it post-workout may aid muscle recovery, the most important factor is maintaining a consistent daily intake.
Why Consistency Matters: To achieve and maintain muscle saturation, regular and consistent supplementation is crucial. Skipping a day or two might slightly slow down the process or reduce effectiveness, but it won't completely undermine your progress. Stick to your routine as much as possible, and if you miss a dose, simply get back on track.
Any Side Effects?
Creatine is generally safe for long-term use, but some people might experience mild bloating or digestive discomfort initially. If this occurs, you can try lowering your dose and gradually increasing it to help your body adjust. Here’s what you need to know:
-
Typical Dosage: Creatine is considered safe at doses of up to 25 grams daily for short periods (up to 14 days) and up to 10 grams daily for long-term use (up to 5 years). Most people find that 3-5 grams daily is sufficient and effective.
-
Possible Side Effects: Some might experience weight gain (mainly lean muscle!), dehydration, upset stomach, or muscle cramps. If you notice any issues, adjusting your dose or consulting a healthcare provider may help.
-
Kidney Health: Creatine can slightly raise creatinine levels in blood tests, but studies show that doses up to 10 grams daily do not impair kidney function in healthy individuals. If you have kidney concerns, consult your doctor before starting creatine.
- Allergic Reactions: There’s some evidence suggesting creatine might exacerbate allergen-induced asthma symptoms, though more research is needed. If you have respiratory issues, check with your healthcare provider.
Wrapping It Up: Creatine Is for More Than Just Muscles
The bottom line? Creatine is not just for athletes or bodybuilders. It’s a versatile, research-backed supplement that offers a range of benefits—from boosting energy levels and brain function to supporting muscle and bone health, especially during and after menopause.
Whether you're looking to get stronger, support your mood, or simply keep your brain sharp, creatine could be the boost you didn’t know you needed. Why not give it a try? You might just find that this little supplement makes a big difference in how you feel day to day.
But as always, it’s important to check with your healthcare provider before trying any new supplement to ensure it’s appropriate for your individual health needs.
Article Links:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33578876/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7998865/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7026167/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7246861/
https://examine.com/supplements/creatine/research/#RQbNpQY-safety-and-toxicology_RQbNpQY-general
https://www.feistymenopause.com/blog/Sports-Supplements-for-Female-Athletes
https://www.drstacysims.com/blog/Why%20Active%20Women%20Need%20Creatine
https://www.womenshealthmag.com/uk/fitness/strength-training/a42178665/creatine/
https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-creatine/art-20347591